

#TRANSFER FILES FROM UBUNTU TO VISUALSVN WINDOWS#
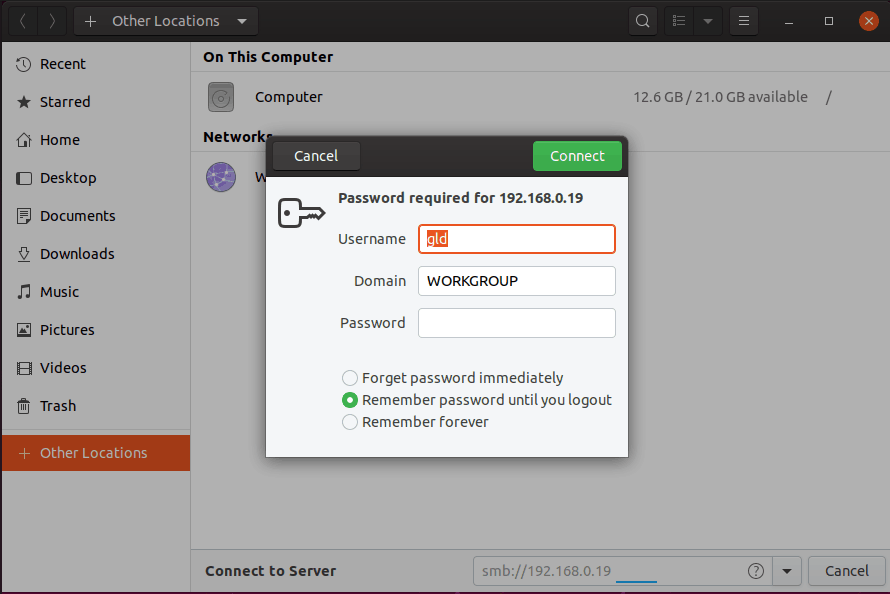
1.1 Accessing Windows Resources from the GNOME Desktopīefore getting into more details of Samba sharing, it is worth noting that if all you want to do is access Windows shared folders from within the Ubuntu GNOME desktop then support is already provided within the GNOME Files application. In this chapter we will look at the steps necessary to share file system resources and printers on an Ubuntu system with remote Windows and Linux systems, and to access Windows resources from Ubuntu. In addition to providing integration between Linux and Windows systems, Samba may also be used to provide folder sharing between Linux systems (as an alternative to NFS which was covered in the previous chapter). This is achieved using technology called Samba. In order for an Ubuntu system to serve such resources over a network to a Windows system and vice versa it must, therefore, support SMB. Windows systems share resources such as file systems and printers using a protocol known as Server Message Block (SMB). Similarly, shared folders and printers residing on Windows systems may also need to be accessible from Ubuntu based systems. It is a common requirement, therefore, that files on an Ubuntu system be accessible to Linux, UNIX and Windows-based systems over network connections. It is also extremely common for Ubuntu and Windows systems to be used side by side in networked environments. It is not surprising therefore that Ubuntu has the ability to act as a file server. Although Linux has made some inroads into the desktop market, its origins and future are very much server-based.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
